What is Thermal Runaway?
Last week’s large battery fire in Queensland has increased the focus on battery safety as we transition to renewables.
We explain lithium-ion risks in this article and we highlight the added safety provided by lithium titanate batteries.
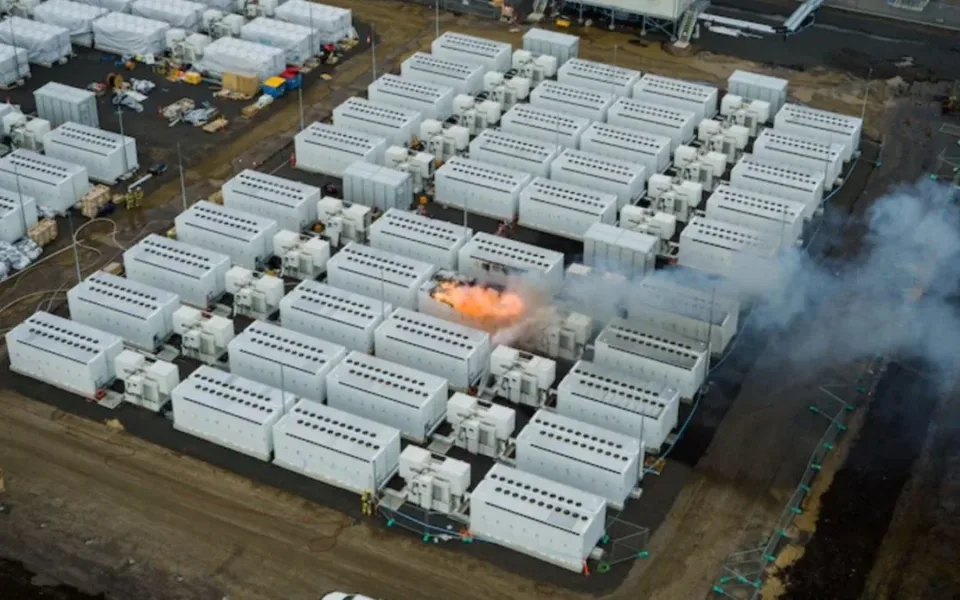
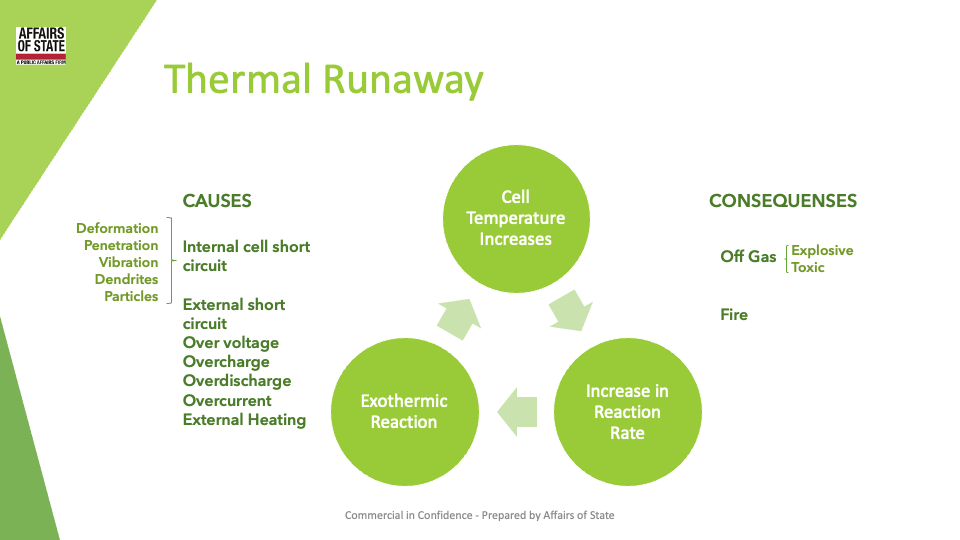
Thermal runaway is a phenomenon in which the lithium-ion cell enters an uncontrollable, self-heating state. Thermal runaway can result in extremely high temperatures, violent cell venting, smoke and fire. It is one of the primary risks related to lithium-ion batteries.
Thermal runaway can be caused by faults in a lithium-ion cell, which can be due to internal failure or external conditions. Some examples of internal failure are defects in the cell that compromise the separator’s integrity, which can cause an internal short circuit. Examples of external conditions are overcharge, multiple over discharges followed by charge, external short circuit, high- and low-temperature environments.
To prevent thermal runaway, lithium-ion batteries should be manufactured with proper quality control and safety features, such as protective circuit boards, battery management systems, and thermal fuses.
Additionally, users should follow the manufacturer’s instructions and avoid exposing the batteries to extreme temperatures, mechanical damage, or incompatible chargers.
Lithium Titanate Batteries
Lithium titanate batteries are an alternate to lithium-ion batteries that use lithium titanate oxide as the anode material, instead of carbon. Lithium titanate batteries have advantages over other lithium-ion batteries, such as faster charging, longer cycle life, lower ownership cost and increased safety.
One of the safety benefits of lithium titanate batteries is that they are less prone to thermal runaway, which is a phenomenon in which the lithium-ion cell enters an uncontrollable, self-heating state that can result in extremely high temperatures, violent cell venting, smoke and fire.
Lithium titanate batteries reduce the risk of thermal runaway by using a different anode material that has a higher thermal stability and a lower reactivity within the electrolyte. This means that the anode does not generate as much heat or gas when it is damaged or abused, and it does not react violently with the electrolyte, which can cause a rapid increase in temperature and pressure. Therefore, lithium titanate batteries can withstand higher temperatures and voltages without triggering thermal runaway.
However, lithium titanate batteries are not completely immune to thermal runaway. They can still experience thermal runaway if they are massively overcharged or exposed to extreme conditions that exceed their tolerance limit. Therefore, lithium titanate batteries should still be manufactured with proper quality control and safety features, such as protective circuit boards, battery management systems, and thermal fuses.
Below is a comparison of some of the technical differentiators between LTO and other lithium ion batteries.

Recent Examples of Thermal Runaway Events in Australia
On July 30, 2021, a Tesla Megapack battery caught fire at a giant battery project in Victoria, Australia. The fire was caused by a fault during testing and took several hours to contain. The fire emitted toxic fumes and prompted an air quality warning for nearby areas.
A fire broke out at the Bouldercombe Battery Project near Rockhampton in central Queensland on Tuesday, September 26, 2023. The fire started in a lithium battery storage unit at 7.45pm and currently causing hazardous smoke in the immediate area. The battery storage facility owned by Genex Power and uses Tesla Megapack 2.0 battery units. The fire was left burning under the supervision of emergency services. The site’s owner and operator says Tesla will be involved in the investigation of the incident. The fire sparked a warning for nearby residents. The incident sparked political debate. Experts warn fires caused by lithium batteries are expected to increase over the coming years as use of the highly flammable product continues to rise.
These and other incidents have raised concerns among firefighters, regulators, and consumers about the safety of lithium-ion batteries and the need for proper standards and guidelines. The United Firefighters Union of Australia has warned the governments to address the fire risks of electric vehicles and battery storage systems, and to provide adequate training and equipment for firefighters. The Australian Government has also announced that it will review the existing regulations and standards for battery safety and performance, and develop a national framework for battery management.
